What happens during duodenal switch surgery?
The ”switch”, or duodenal switch procedure, is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that combines qualities of both the sleeve gastrectomy and the gastric bypass.
The operation, often referred to as DS surgery, is performed in two steps. First, we conduct a sleeve gastrectomy, removing around 80 percent of the stomach and converting the remainder into a slender tube, or gastric sleeve. We then divide the small bowel that normally connects to the stomach (called the duodenum) to create the bypass. Consumed food would normally go from the sleeve into the initial part of the small intestine, but it is re-routed or ”switched” to the lower part of the small intestine.
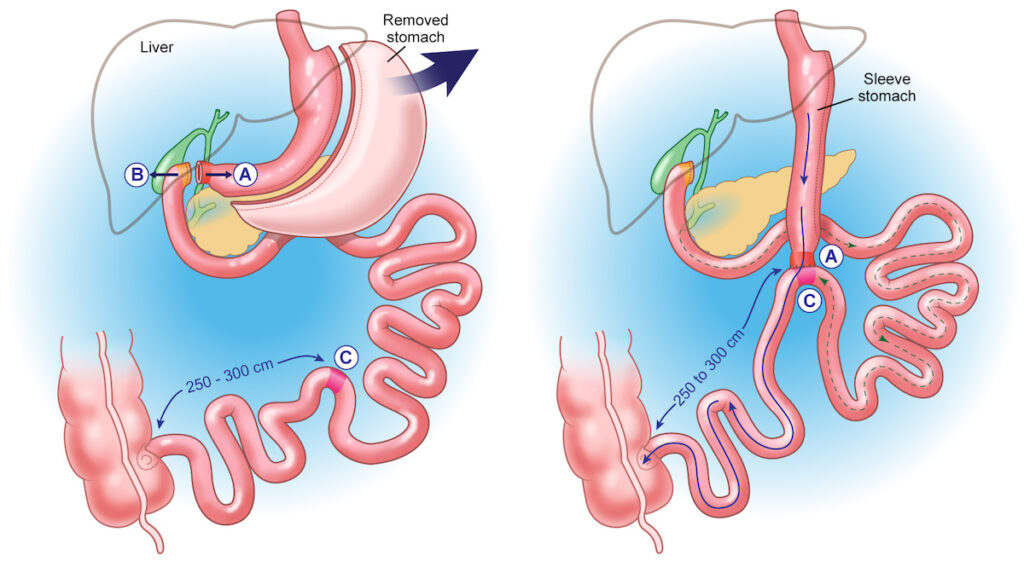
While considered a complex procedure due to its surgical intricacies, there are several ways to go about the bypass part of the operation. At BMI of Texas, we perform a single anastomosis switch, where we bypass a significant length of the small intestine (much more than with gastric bypass) and then create a single connection between the bottom of the sleeve and the small bowel.
Of the four bariatric procedures we offer, this is the most drastic. As a result, it creates the most significant weight loss and offers the greatest chance of having additional health benefits, like better controlling or eliminating Type 2 diabetes.
How much weight will I lose after duodenal switch surgery?
The duodenal switch procedure results in greater, more rapid weight loss than other weight loss procedures. It also improves a patient’s chances of keeping the weight off by decreasing caloric intake, reducing absorption, and changing the hormonal balance in the GI tract.
Why should I consider loop duodenal switch surgery?
Generally, high-BMI (>50) diabetic patients are best suited for this procedure. However, it is widely known across all areas of modern medicine that obesity raises the risk of disease in nearly every system in the human body. Duodenal switch surgery can actively help reduce the risk and the effects of developing these diseases, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases: hypertension, arterial disease, vascular disease, heart attack, stroke
- Respiratory diseases: asthma, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity hypoventilation syndrome
- Metabolic diseases: hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance and diabetes
- Gastrointestinal diseases: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Reproductive diseases: polycystic ovary syndrome, infertility
- Musculoskeletal pain: back strain, weight-bearing osteoarthritis
- Cancer: especially colorectal cancer and liver cancer
What are the dangers of duodenal switch surgery?
Like any other surgery, the DS procedure carries certain risks, which can include internal bleeding, infection, blood clots, and hernias. Risks associated with any abdominal surgery can also include excessive bleeding, adverse reactions to anesthesia, breathing problems, or leaks in your gastrointestinal system. You may also experience changes as your body reacts to rapid weight loss in the first three to six months, including body aches, flu-like symptoms, fatigue, dry skin, thinning hair, and mood changes. Longer term risks and complications associated with DS surgery could include bowel obstruction, nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, gallstones, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), malnutrition, stomach perforation, ulcers, bile reflux, diarrhea or frequent bowel movements and less likely vomiting.
As is the case with all medical procedures, surgical complications can result in fatalities, and while extremely rare in occurrence, your medical condition and long-term history will be carefully assessed to mitigate any and all risk factors. But that’s only the beginning of our process to ensure your safe, successful, and long-lasting results. Our medical staff follows detailed pre and post surgical guidelines, which include rigorous candidacy assessments and multi-step precautions during surgery, as well as several in-person visits and careful monitoring of your weight loss experience once you leave our doors to begin your newer, healthier life.
How long is recovery from duodenal switch surgery?
Patients are usually kept in the hospital for one to three days following surgery, then a few weeks of additional recovery time at home. Your surgeon will want to see you for a follow-up visit two weeks after surgery, and then you will need to get onto a regular BMI of Texas follow-up schedule. During your recovery, your body will be going through huge changes, including rapid weight loss, and any severe symptoms should be reported to your BMI care team immediately.
You’ll also have very specific dietary guidelines during recovery, including not only what you can eat, but how you eat as well. These precautions are implemented to give your digestive system time to heal and adjust to its new digestive process. This transition phasetypically takes one to two weeks, and may primarily include liquids and soft foods as you return to your normal diet.
Thanks to advances in BMI’s DS surgical procedures, you will likely not experience dumping syndrome, which occurs when food, especially sugar, moves too quickly from the stomach to the duodenum. You will need to take additional regular daily vitamins (even more than other surgery patients) for the rest of your life. If you stop taking any prescribed vitamins, you will be more likely to develop a vitamin, mineral, or other nutritional deficiency.
To the average person, not getting enough vitamins may not sound like a big deal. However, when you “change the plumbing” with a duodenal switch, it can become a life-threatening problem. Nutritional complications with the duodenal switch include deficiencies in protein, iron, calcium, copper, zinc and fat-soluble vitamins. You may be asked to eat differently if protein deficiency is to occur.
Bowel movement changes are also more common with the DS than with other types of surgery. On average, DS patients will experience two to five bowel movements per day, but some patients have more. It is also not uncommon to have problems with diarrhea or loose stools, as well as foul-smelling stools or flatulence.

The board certified team at BMI of Texas will prescribe supplements after surgery, such as:
- Multi-vitamin/mineral support
- Additional calcium
- Additional iron
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A,D,E, and K)
- Probiotics (beneficial bacteria found the intestinal tract)
How do I begin?
If you are interested in learning more about San Antonio duodenal switch surgery, contact BMI of Texas at 210-405-6424.


